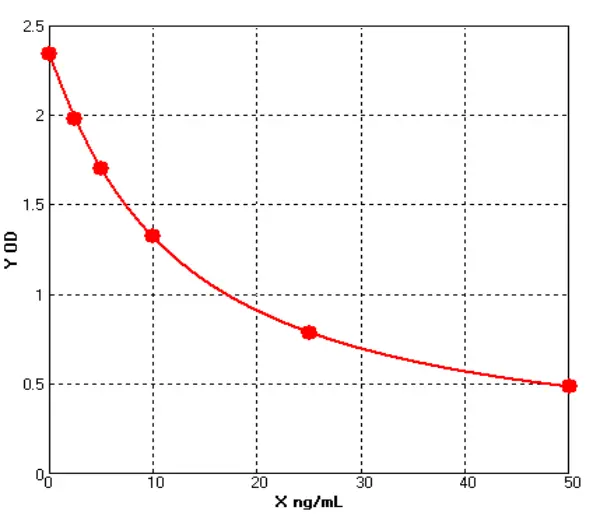
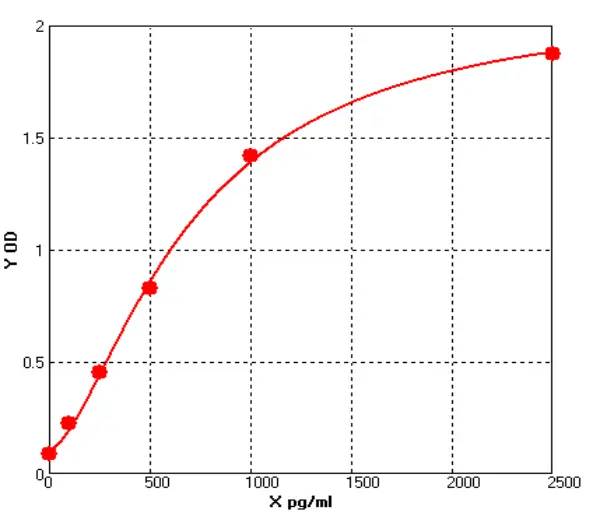
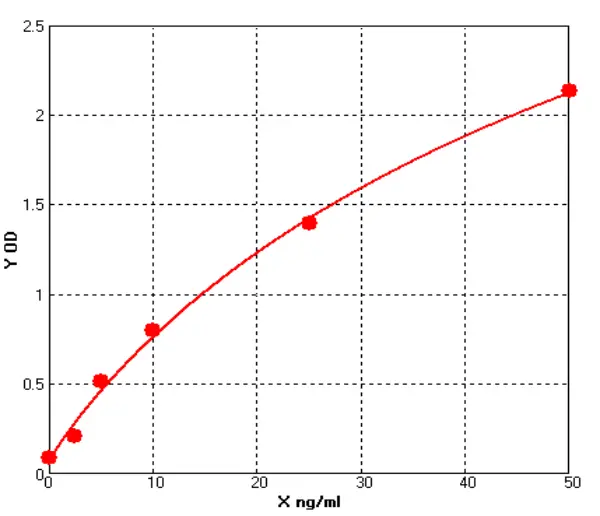
- Host Cell Protein Detection Kits
- Host Cell DNA Residue Detection Kits
- Antibodies
- Recombinant Proteins
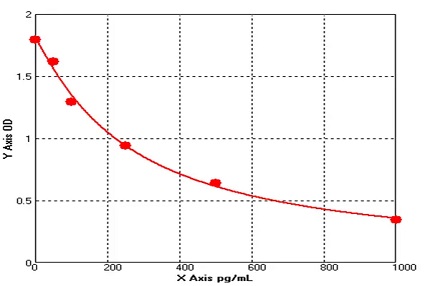
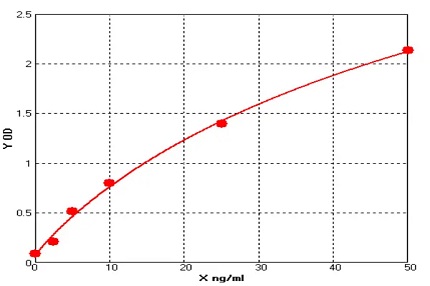
- ELISA Kits
- Cellular Component Protein Library
- Plasmids
- Promotions
-
Monitoring Chronic Diseases Using BFGF ELISA Kit
Chronic diseases pose a significant challenge to global health, often accompanied by long-term inflammation, tissue damage, and repair processes. In the study of these diseases, basic fibroblast growt...
Apr.16, 2025Read More > -
The Need for Methamphetamine Residue Detection
Methamphetamine, as a commonly abused drug, has seen increasing concern over its residue in food and pharmaceuticals. With the growing threat of drug abuse to public safety and health, regulatory agen...
Apr.14, 2025Read More > -
Advances in ELISA Technology: A Case Study of Human Hepcidin
The balance of iron metabolism is crucial for human health, and human hepcidin plays a key role in regulating iron levels in the body. In recent years, ELISA technology has been widely used in iron me...
Apr.12, 2025Read More >
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology focuses on clarifying the essence of life. It mainly studies the structure and function of biological macromolecular nucleic acids and proteins and the transmission and regulation of life information. The main research contents include the molecular biology of nucleic acid, molecular biology of protein and molecular biology of cell signal transduction.
Molecular biology has developed rapidly since the middle of the 20th century. One of the most important reasons is the progress of gene operation and gene engineering technology. Basic operations include: cutting and joining of DNA, nucleic acid hybridization, gel electrophoresis, cell transformation, nucleic acid sequence analysis, artificial gene synthesis, site-directed mutagenesis and PCR amplification. This is the core technology of molecular biology research. Genetic engineering refers to inserting nucleic acid molecules into vector molecules in vitro to make them enter host cells for continuous and stable reproduction and expression. The ability to cross the barrier of natural species and place genes from any organism in new host biological cells without kinship is the fundamental feature that distinguishes genetic engineering technology from other technologies.