Phage Display
Service Introduction:
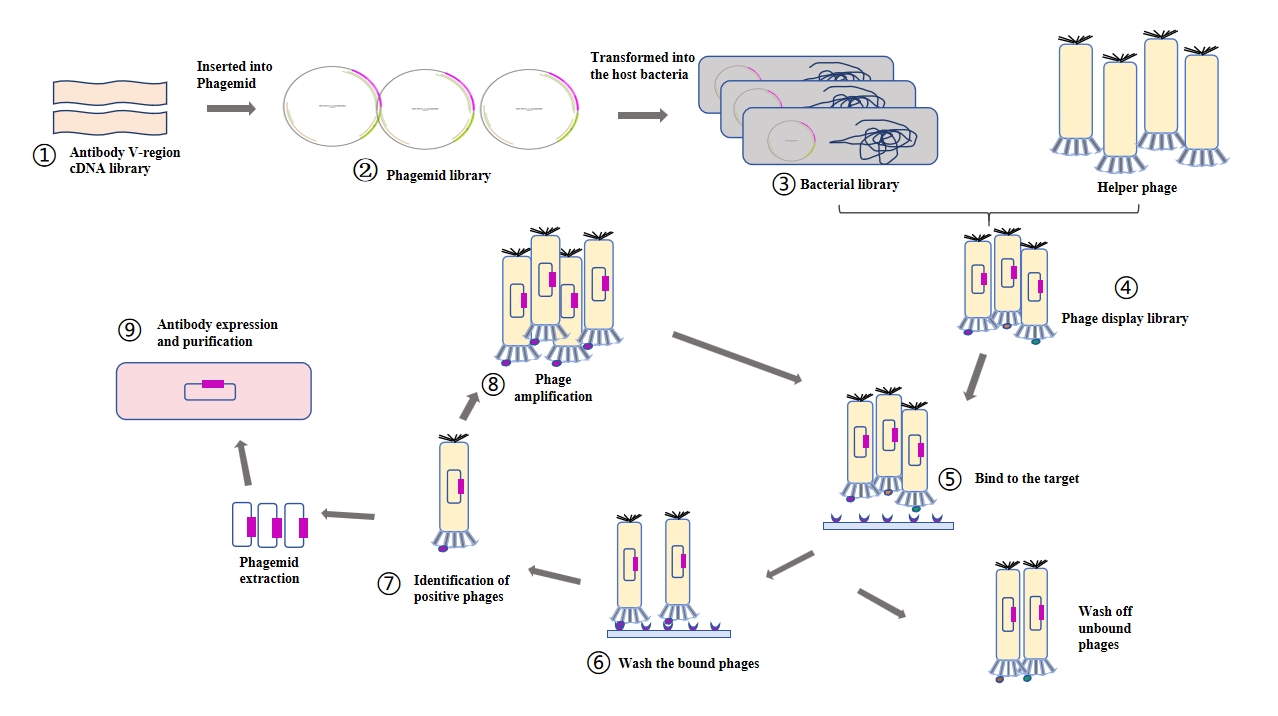
Phage display technology involves fusing the gene of an exogenous protein or peptide with a phage capsid protein gene via genetic engineering, allowing the phagemid to display the encoded protein while retaining the gene within the phagemid. This establishes a linkage between phenotype and genotype. Through high-throughput screening and enrichment, recombinant proteins or peptides capable of recognizing target molecules can be obtained in vitro. In antibody library research, this method allows in vitro screening of B-cell antibody libraries derived from animals such as mice, rabbits, and sheep. This avoids complex cell fusion procedures, shortens the time required to obtain antibodies, and offers advantages including high stability, large library capacity, and methodological simplicity.
Basic Category of Antibody Libraries:
Naive Antibody Library: Built using non-immunized lymphocytes, leveraging naturally rearranged variable region genes to construct libraries with capacities up to 10¹¹.
Immune Antibody Library: Constructed from B cells or tissues of animals or humans that have been immunized with specific antigens. Immune libraries typically have smaller scales but contain a higher abundance of antigen-specific antibodies, facilitating the selection of high-affinity antibodies.
Semi-Synthetic Antibody Library: Built by combining partially synthetic sequences with natural sequences. The first semi-synthetic antibody libraries used various framework genes to maintain high diversity within the library.
Synthetic Antibody Library: An antibody library with variable region sequences entirely synthesized artificially.
Screening Process:
Service Advantages:
1. The positive insertion rate of library reaches 95%.
2. Library capacity reaches 10⁷.
3. Flexible screening strategies and various methods enable rapid delivery.
Service Details:
Service Period: 8-10 weeks (excluding immunization)
Including both kappa and lambda light chain subtypes in coverage.
Library Capacity: ≥ 10⁷
| No. | Library Type | Species | Library Category | Antibody Gene Source | Tag | Capacity |
| 1 | scFv | Rabbit | Immune | Peripheral Blood | His/HA | ≥ 10⁷ |
| 2 | scFv | Rabbit | Semi-Synthetic | ≥ 10⁹ | ||
| 3 | scFv | Sheep | Immune | ≥ 10⁷ | ||
| 4 | scFv | Sheep | Semi-Synthetic | ≥ 10⁹ |
Final Deliverables:
1. Phage-ELISA testing on selected monoclonal clones, with positive clones defined as those with readings 2.1 times higher than blank and negative controls, followed by sequencing.
2. ELISA testing on positive clones with different sequences, delivering at least 3 clones.
3. If results are unsatisfactory, an alternative screening method and strategy will be employed for 3-4 rounds, followed by further testing of monoclonal clones to determine if new clones or clones with higher affinity emerge. If new clones appear, further experiments will continue; otherwise, project-specific issues will be considered.