Search ELISA Kits
Growth Factor Proteins Types
-
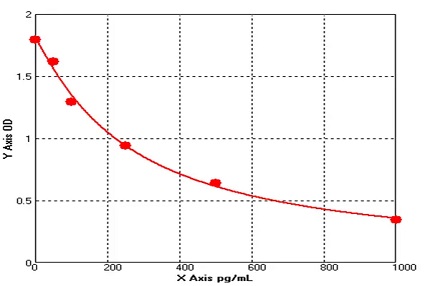
P01E0032P-T Human Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) Protein,Recombinant
Cat. No.: P01E0032P-T
Expression Host: E.coli
Expression Region: Asn971-Arg1023
Fusion Tag: 6×xHis-SUMO (N-terminus)
-
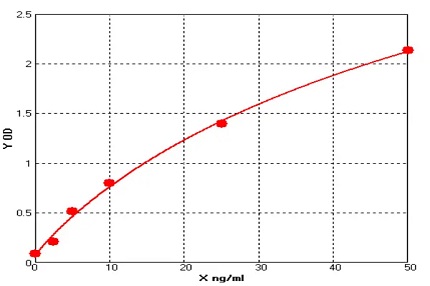
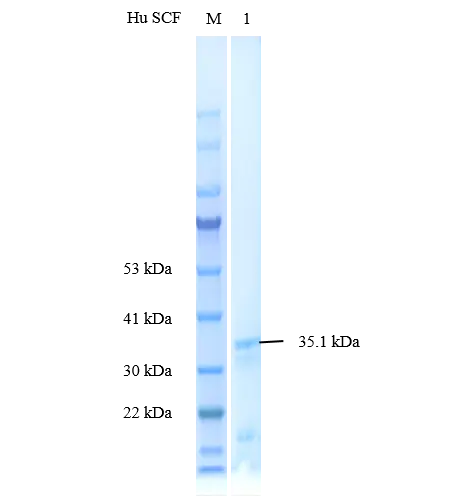
P01S0011P-T Human Stem Cell Factor (SCF) Protein, Recombinant
Cat. No.: P01S0011P-T
Uniprot No.: P21583
Expression Host: E.coli
Expression Region: Met1-Ala189
Fusion Tag: SUMO (N-terminus), 6×His (C-terminus)
-
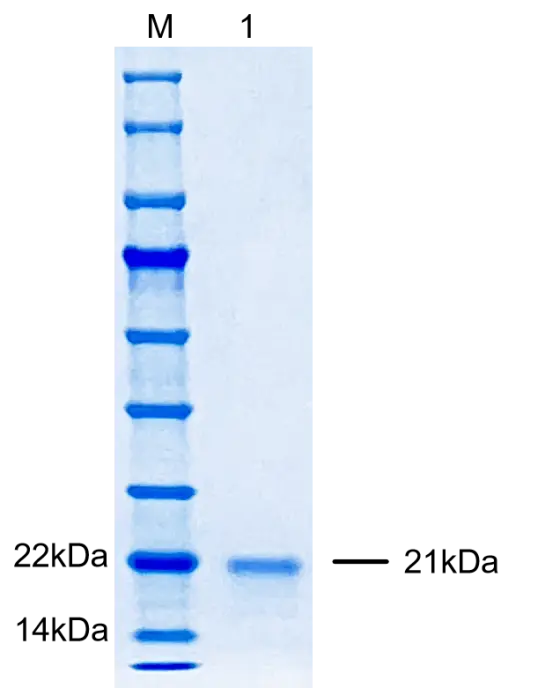
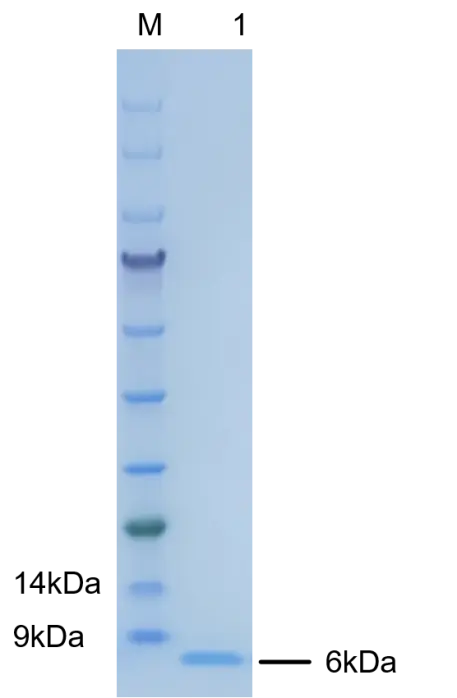
P01E0032P Human Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) Protein,Recombinant
Cat. No.: P01E0032P
Expression Host: E.coli
Expression Region: Asn971-Arg1023
Fusion Tag: None
-
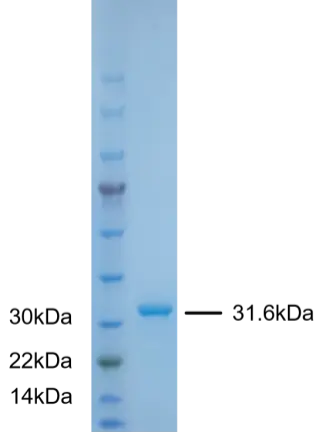
P01F0003P-T Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 (FGF2) Protein, Recombinant
Cat. No.: P01F0003P-T
Uniprot No.: D9ZGF5
Expression Host: E.coli
Expression Region: Met1-Ser155
Fusion Tag: 6×His-SUMO (N-terminus)
-
P01F0003P Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 (FGF2) Protein, Recombinant
Cat. No.: P01F0003P
Uniprot No.: D9ZGF5
Expression Host: E.coli
Expression Region: Met1-Ser155
Fusion Tag: None

-
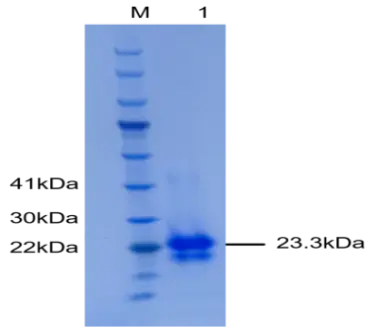
P01V0016P-T Human Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor 165 (VEGF165) Protein, Recombinant
Cat. No.: P01V0016P-T
Uniprot No.: P15962-4
Expresion Host: 293T
Expression Region: Ala27-Arg191
Fusion Tag: 6×His (C-terminus)
Growth Factor Proteins FAQs
-
Q
What is growth factor protein?
Growth factors are necessary to regulate the normal growth and metabolism of microorganisms, but they cannot be synthesized by themselves with simple carbon and nitrogen sources. In a broad sense, it includes vitamins, bases, purines, pyrimidines, biotins, niacin, etc. Generally, growth factors are peptide hormones, including insulin, epidermal growth factor (EGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), and somatostatin released by growth hormon (somatostatin=SRIH). It is a kind of polypeptide substance with multiple effects such as regulating cell growth and other cell functions by binding to specific, high-affinity cell membrane receptors. It exists in platelets, various adult and embryonic tissues and most cultured cells, and has certain specificity for different types of cells. Generally, the growth of cultured cells requires the coordination of multiple growth factors. Tumor cells have the characteristics of independent growth factors.
-
Q
Growth factor proteins function
Growth factors usually have the functions of stimulating cell proliferation, damage repair and cell differentiation. It is a secreted protein or hormone that plays an important role in regulating intracellular processes. It is an important signal molecule between cells. For example, cytokines and hormones can bind to specific receptors on the surface of target cells.