Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL) can also be called TNFSF11; ODF; OPGL; RANKL; TRANCE
Specifications Of P01R0005 Human Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL) Protein, Recombinant
| Product Information | |
catalog number | P01R0005 |
Package Size | 10ug/50ug/500ug/1mg |
Other Names | TNFSF11; ODF; OPGL; RANKL; TRANCE |
Protein & NCBI Number | O14788, AF019047.1 |
Host | E.coli |
Express Region | Ile140-Asp317 |
Protein Sequence | IRAEKAMVDGSWLDLAKRSKLEAQPFAHLTINATDIPSGSHKVSLSSWYHDRGWAKISN |
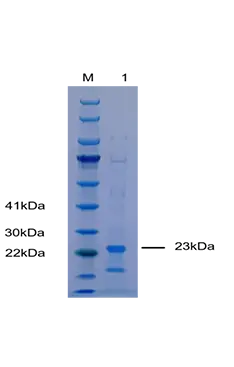
Molecular Weight | The protein molecule consists of 299 amino acids (including the fusion tag), |
Fusion Tag | 6xHis-SUMO (N-terminus) |
Purity | ≥90% SDS-PAGE |
Physical Property | Liquid |
Components | 0.01M PBS+20% glycerol, sterile solution |
Storage & Stability | After aliquoting, the stability of the samples can be maintained for up to 6 |
Applications | Antibody preparation, immunoassay (ELISA, WB), subcellular localization and interaction protein identification, etc. |
Lead Time | 5 to 10 business days; 2 to 3 days for stock products |
Background |
Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL), also known as tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11, osteoclast differentiation factor (ODF), CD254, osteoprotegerin ligand (OPGL), and tumor necrosis factor-related activation-induced cytokine (TRANCE). It acts as a differentiation and activation factor for osteoclasts, enhancing the ability to stimulate proliferation of naïve T cells as a cytokine by binding to TNFRSF11B/OPG and TNFRSF11a/RANK. It may also serve as a critical regulator of interactions between T cells and dendritic cells, potentially modulating T cell-dependent immune responses and enhancing bone resorption in malignancy-associated hypercalcemia. RANKL induces osteoclastogenesis by activating multiple signaling pathways in osteoclast precursor cells, notably inducing sustained oscillations in intracellular Ca2+ concentrations that activate NFATC1. NFATC1 translocates to the nucleus and induces transcription of osteoclast-specific genes, promoting osteoclast differentiation. During osteoclast differentiation, activation of CREB1 and generation of mitochondrial ROS dependent on TMEM64 and ATP2A2 are essential for osteoclastogenesis. Expression is highest in peripheral lymph nodes, with weaker expression in the spleen, peripheral blood leukocytes, bone marrow, stomach, heart, thyroid, placenta, and skeletal muscle. |
BlueGene Biotech Product Show
Related Products Of Human Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL) Protein, Recombinant
P01I0420 Human Long arginine 3-IGF-1 (IGF1-LR3) Protein,Recombinant
P01I0345 Human Interferon gamma (IFNγ) Protein, Recombinant