Tumor Necrosis Factor α (TNF α) can also be called DIF; TNFA; TNFSF2; TNLG1F; TNF-alpha
Specifications Of P03T0008 Mouse Tumor Necrosis Factor α (TNF α) Protein, Recombinant
| Product Information | |
catalog number | P03T0008 |
Package Size | 10ug/50ug/500ug/1mg |
Other Names | DIF; TNFA; TNFSF2; TNLG1F; TNF-alpha |
Protein & NCBI Number | P06804、NM_013693.3 |
Host | E.coli |
Express Region | Leu 80-Leu 235 |
Protein Sequence | LRSSSQNSSDKPVAHVVANHQVEEQLEWLSQRANALLANGMDLKDNQLVVPADGLYLVYSQ |
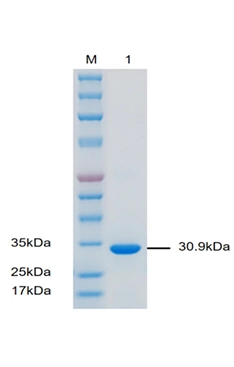
Molecular Weight | The protein molecule consists of 277 amino acids (including the fusion tag), with a |
Fusion Tag | 6xHis-SUMO (N-terminus) |
Purity | ≥90% SDS-PAGE |
Physical Property | Liquid |
Components | 0.01M PBS+20% glycerol, sterile solution. |
Storage & Stability | After aliquoting, the stability of the samples can be maintained for up to 6 months |
Applications | Antibody preparation, immunoassay (ELISA, WB), subcellular localization and |
Lead Time | 5 to 10 business days; 2 to 3 days for stock products |
Background |
The TNF-α gene encodes a multifunctional pro-inflammatory cytokine that is a member of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily. It is primarily secreted by macrophages and exerts its functions by binding to tumor necrosis factor receptors. The tumor necrosis factor and tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily proteins (TNFR SFP) are a group of ligand-receptor protein superfamilies. TNF contains a trimeric symmetric structural motif called the tumor necrosis factor homology domain (THD), which can bind to the cysteine-rich domains (CRDs) in TNF receptors (TNFRs). The diversity of CRDs leads to the heterogeneity of TNFRs. The activity of TNF-α is mediated by its two receptors, TNF-R1 (p55) and TNF-R2 (p75), which have distinct signaling activities. TNF-R1 is generally pro-apoptotic, while TNF-R2 is usually anti-apoptotic. TNF-R1 and TNF-R2 have similar extracellular TNF-binding structures characterized by four repeated cysteine-rich domains, but they have different intracellular domains. The main structural differences between TNF-R1 and TNF-R2 lead to differences in their biological activities, primarily due to the lack of an intracellular death domain in TNF-R2. TNF-α is pleiotropic and has been demonstrated to regulate a variety of inflammatory and autoimmune processes. Low levels of TNF-α can modulate the body’s immune response to act against infections, while high levels of TNF-α induce the secretion of other inflammatory factors such as IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12, and promote inflammation within the body. TNF-α can kill tumors by promoting T cell proliferation and damaging vascular endothelial cells, as well as by recruiting immune cells, inducing the production of prostaglandins and cyclooxygenases, and inducing oxidative stress, thereby promoting cell degeneration and the progression of inflammation. |
BlueGene Biotech Product Show
Related Products Of Related Products Of Human Interleukin 1β (IL-1β) Protein, Recombinant
P01T0008 Human Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) Protein, Recombinant