- Host Cell Protein Detection Kits
- Host Cell DNA Residue Detection Kits
- Antibodies
- Recombinant Proteins
- ELISA Kits
- Cellular Component Protein Library
- Plasmids
- Promotions
-
Exhibition review | The 6th BIONNOVA BioPharma Innovators Summit & Expo Successfully Concluded at Shanghai Science Hall on April 9-10, 2025
Symposium HighlightsThe summit comprehensively addressed critical topics across biopharmaceutical R&D and manufacturing, including:Therapeutics Development: Antibody drugs, antibody-drug conjugate...
Apr.24, 2025Read More > -
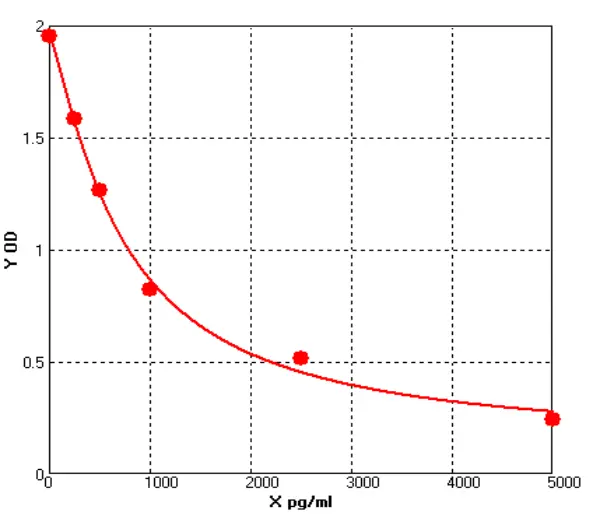
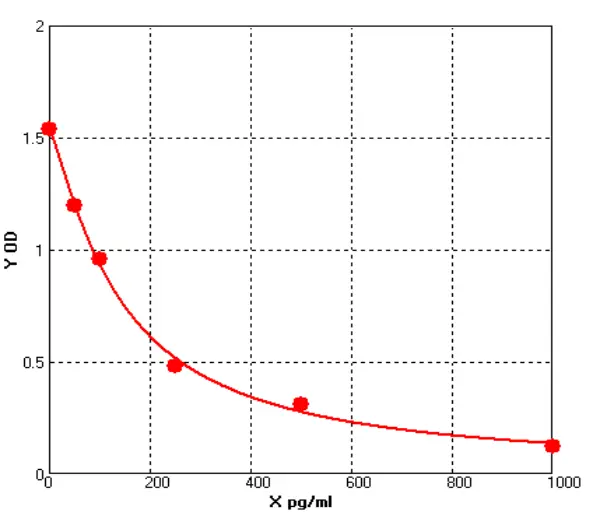
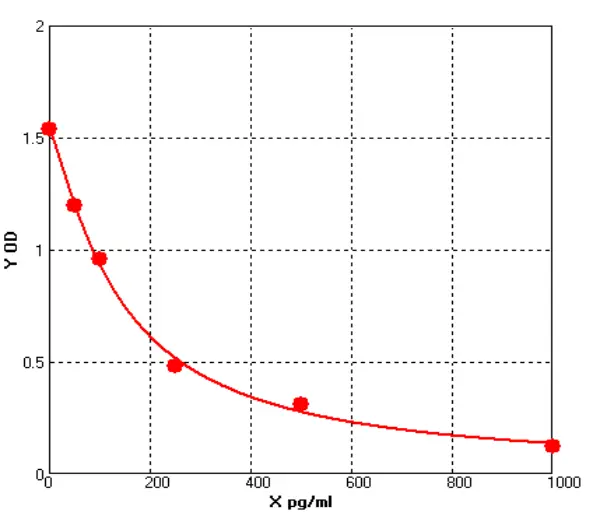
Epinephrine ELISA: Sensitive and Reliable Quantification of Epinephrine
Principle of the Epinephrine ELISAThe Epinephrine ELISA can be used for the in vitro quantitative detection of epinephrine in human plasma and urine. The Epinephrine ELISA utilizes a sandwich method p...
Apr.24, 2025Read More > -
NS0 Host Cell DNA Origin and Control
NS0 host cell DNA refers to the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of NS0 cells (mouse myeloma cell line) used as hosts in the production of biological products (such as antibodies and other protein drugs).N...
Apr.22, 2025Read More >
BlueGene Biotech's Research For Signal Transduction
1. Definition Of Signal Transduction
It is known that there are many signal transduction modes and pathways in cells, and there are multiple levels of cross-regulation between them. It is a very complex network system. In short, a process in which various signals can enter the cell through the cell membrane and gradually cause changes in cellular substances, mainly proteins, is called signal transduction. It is a multi-enzyme cascade reaction process. Each signal pathway forms a highly ordered regulatory network in vivo through the interaction of intercellular signal proteins.
2. Mammals & Signal Transduction
Mammals need a variety of signal transduction pathways to maintain the integrity and coordination of cell response to signal stimulation. There are mainly six kinds of transmitters responsible for extracellular signal transduction to the interior of cells. They include ion channel gates, receptor enzymes, serpentine receptors, steroid receptors, adhesion receptors, and receptors themselves that do not contain enzymes.