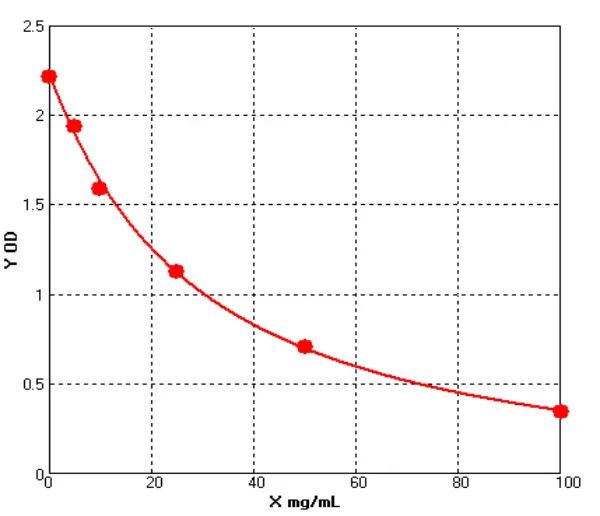
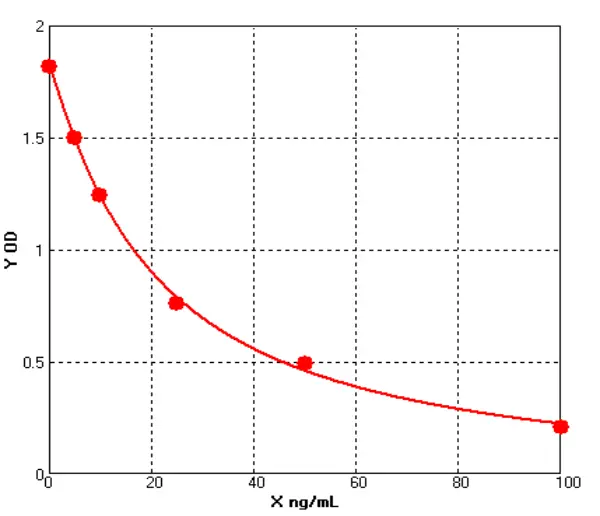
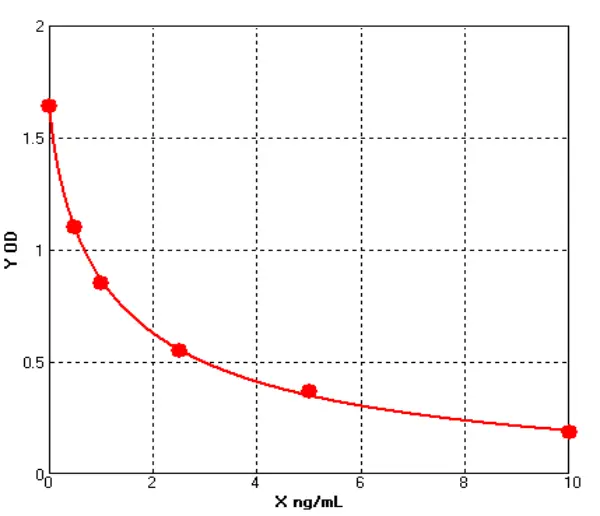
- Host Cell Protein Detection Kits
- Host Cell DNA Residue Detection Kits
- Antibodies
- Recombinant Proteins
- ELISA Kits
- Cellular Component Protein Library
- Plasmids
- Promotions
-
Collagen 1 ELISA: Principle, Advantages, and Clinical Applications
The principle of the Collagen 1 ELISA is to use the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) technology to quantitatively detect the ColⅠcontent in samples through a double-antibody sandwich method....
Apr.18, 2025Read More > -
Monitoring Chronic Diseases Using BFGF ELISA Kit
Chronic diseases pose a significant challenge to global health, often accompanied by long-term inflammation, tissue damage, and repair processes. In the study of these diseases, basic fibroblast growt...
Apr.16, 2025Read More > -
The Need for Methamphetamine Residue Detection
Methamphetamine, as a commonly abused drug, has seen increasing concern over its residue in food and pharmaceuticals. With the growing threat of drug abuse to public safety and health, regulatory agen...
Apr.14, 2025Read More >
BlueGene Biotech's Research For Immunology
1. Four Periods Of Immunology
It is generally believed that the development of immunology has experienced four periods: empirical immunology, classical immunology, modern immunology and modern immunology period. Immunology is one of the forefront positions of life science and modern medicine. The human immune system performs immune functions. The immune system includes immune organs, immune cells and immune molecules.
2. Immune Function Of Modern Immunology
Modern immunology proposes that the immune function of the body is the response to antigenic stimulation, and the immune response is manifested in the ability of the immune system to recognize itself and eliminate non-self. Immune function functions according to immune recognition. This function includes immune defense against exogenous foreign bodies (mainly infectious factors), removal of the immunity of decayed or damaged cells to maintain their own stability and eliminate of immune surveillance of mutant cells.