- Host Cell Protein Detection Kits
- Host Cell DNA Residue Detection Kits
- Antibodies
- Recombinant Proteins
- ELISA Kits
- Cellular Component Protein Library
- Plasmids
- Promotions
-
Exhibition review | The 6th BIONNOVA BioPharma Innovators Summit & Expo Successfully Concluded at Shanghai Science Hall on April 9-10, 2025
Symposium HighlightsThe summit comprehensively addressed critical topics across biopharmaceutical R&D and manufacturing, including:Therapeutics Development: Antibody drugs, antibody-drug conjugate...
Apr.24, 2025Read More > -
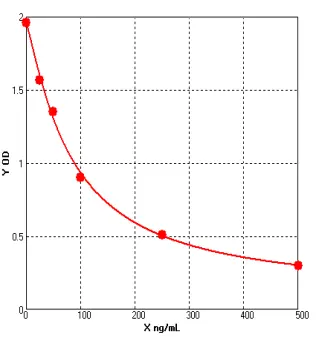
Epinephrine ELISA: Sensitive and Reliable Quantification of Epinephrine
Principle of the Epinephrine ELISAThe Epinephrine ELISA can be used for the in vitro quantitative detection of epinephrine in human plasma and urine. The Epinephrine ELISA utilizes a sandwich method p...
Apr.24, 2025Read More > -
NS0 Host Cell DNA Origin and Control
NS0 host cell DNA refers to the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of NS0 cells (mouse myeloma cell line) used as hosts in the production of biological products (such as antibodies and other protein drugs).N...
Apr.22, 2025Read More >
Immunology
The immune response is a physiological process produced by the immune system to eliminate antigens. This process is the comprehensive embodiment of the physiological functions of various parts of the immune system, including a series of physiological reactions such as antigen presentation, lymphocyte activation, immune molecule formation, and immune effect.
Immunity is the capability of the body's immune system to recognize self and foreign antigens and to eliminate antigenic foreign bodies through immune responses to maintain the body's physiological balance. The functions of immunity include immune defense, immune stabilization, and immune surveillance. The immune system is a complex network of specialized cells, tissues, organs of immune function, and nuclear molecules that recognizes self and non-self in any higher animal, elicits immune responses, perform immune effects, and maintain its own stability and is the material basis of the immune mechanism of the body. Immune organs include: central immune organs (such as bone marrow, thymus, and other functional organs), peripheral immune organs (such as lymph nodes, spleen, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue, etc.)