- Host Cell Protein Detection Kits
- Host Cell DNA Residue Detection Kits
- Antibodies
- Recombinant Proteins
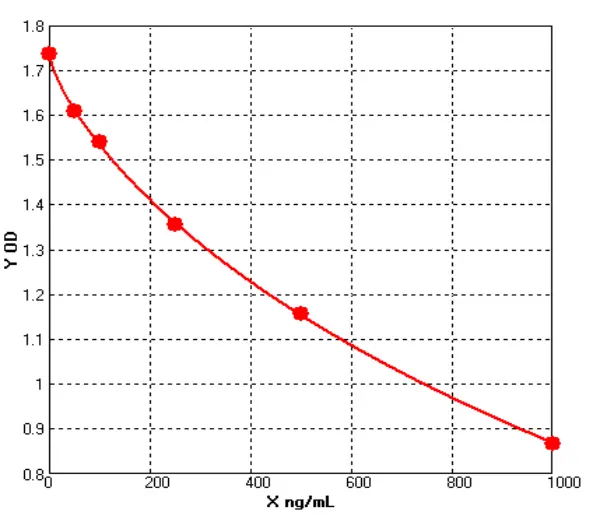
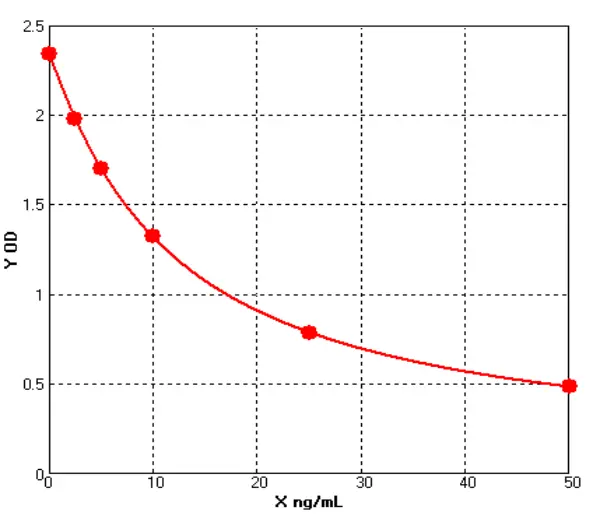
- ELISA Kits
- Cellular Component Protein Library
- Plasmids
- Promotions
-
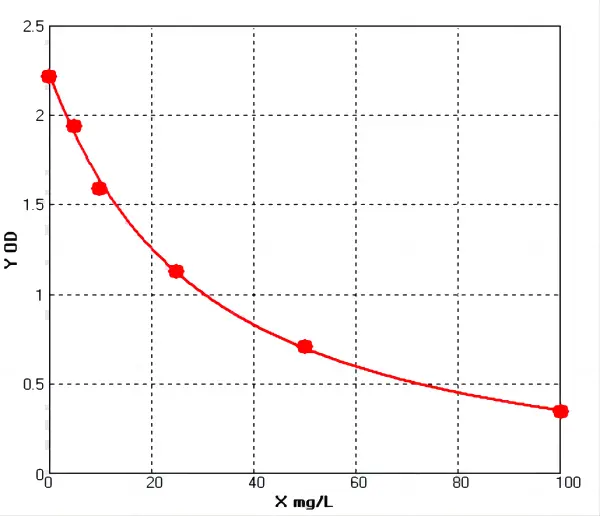
Collagen 1 ELISA: Principle, Advantages, and Clinical Applications
The principle of the Collagen 1 ELISA is to use the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) technology to quantitatively detect the ColⅠcontent in samples through a double-antibody sandwich method....
Apr.18, 2025Read More > -
Monitoring Chronic Diseases Using BFGF ELISA Kit
Chronic diseases pose a significant challenge to global health, often accompanied by long-term inflammation, tissue damage, and repair processes. In the study of these diseases, basic fibroblast growt...
Apr.16, 2025Read More > -
The Need for Methamphetamine Residue Detection
Methamphetamine, as a commonly abused drug, has seen increasing concern over its residue in food and pharmaceuticals. With the growing threat of drug abuse to public safety and health, regulatory agen...
Apr.14, 2025Read More >
Cell Signal Transduction
Signal ligand molecules activate the receptor domain in the cell by binding to the specific domain outside the receptor protein membrane on the cell membrane, so as to transfer the signal from outside the membrane to inside the membrane. This process is called cell signal transduction.
Cell information transmission methods: (1) through direct contact between adjacent cells; (2) through the secretion of various chemical substances by cells to regulate the metabolism and functions of other cells; the chemical substances that regulate the life activities of cells are called information substances. Intercellular information substances are the collective name of chemical substances secreted by cells that regulate the life activities of target cells, also known as first messengers. Mainly include proteins and peptides (such as growth factors, cytokines, insulin, etc.), amino acids and their derivatives (such as glycine, thyroxine, epinephrine, etc.), steroid hormones (such as glucocorticoids, sex hormones, etc.), fatty acids Derivatives (eg prostaglandins), gases (eg nitric oxide, carbon monoxide, etc.).